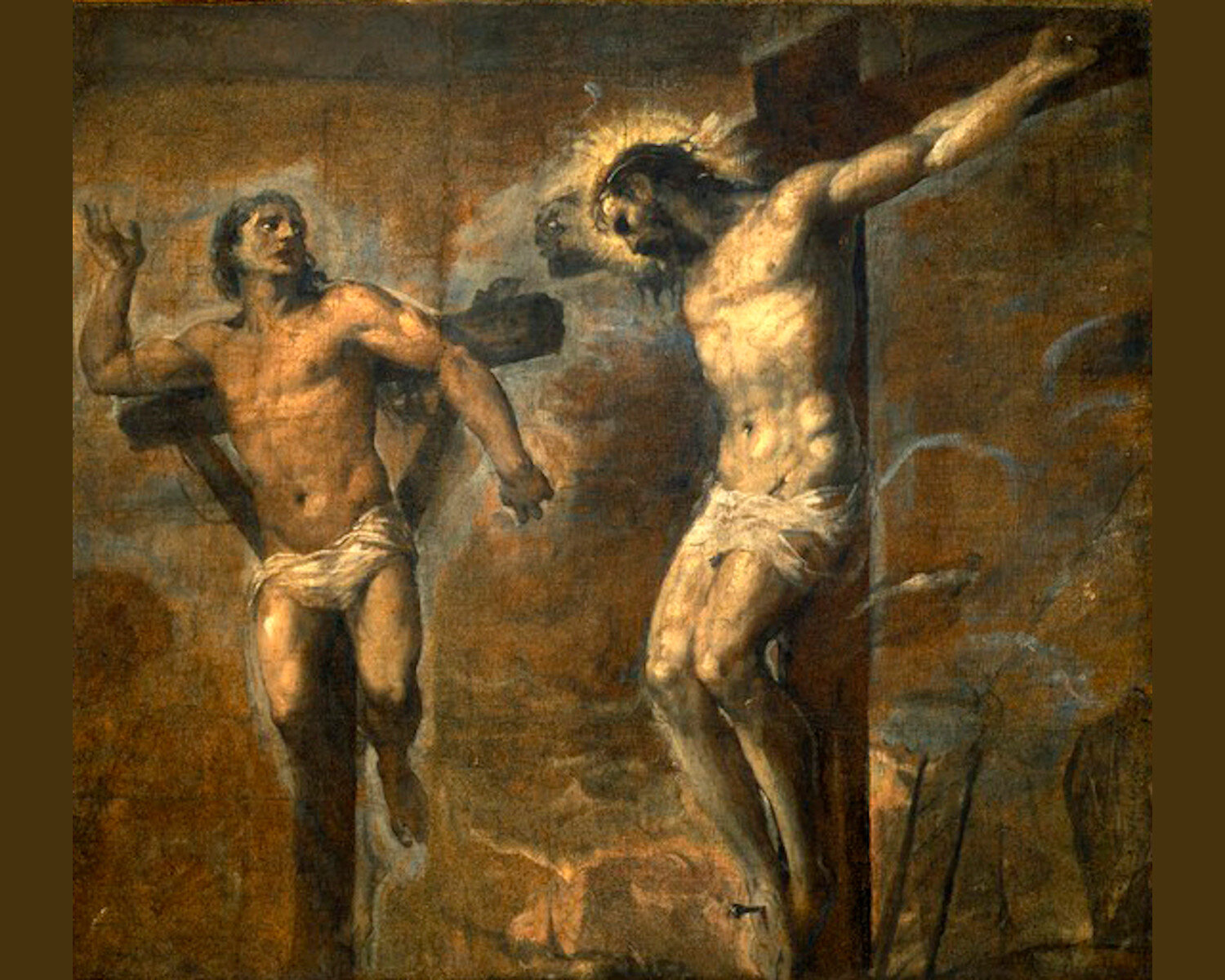“There are few authentic prophetic voices among us, guiding truth-seekers along the right path. Among them is Fr. Gordon MacRae, a mighty voice in the prison tradition of John the Baptist, Maximilian Kolbe, Alfred Delp, SJ, and Dietrich Bonhoeffer.”
— Deacon David Jones
“I Am a Mystery to Myself.” The Last Days of Padre Pio
For half the 20th Century, Saint Padre Pio suffered the wounds of Christ. All of them, including the cynicism of doubt and the tyranny of false witness.
For half the 20th Century, Saint Padre Pio suffered the wounds of Christ. All of them, including the cynicism of doubt and the tyranny of false witness.
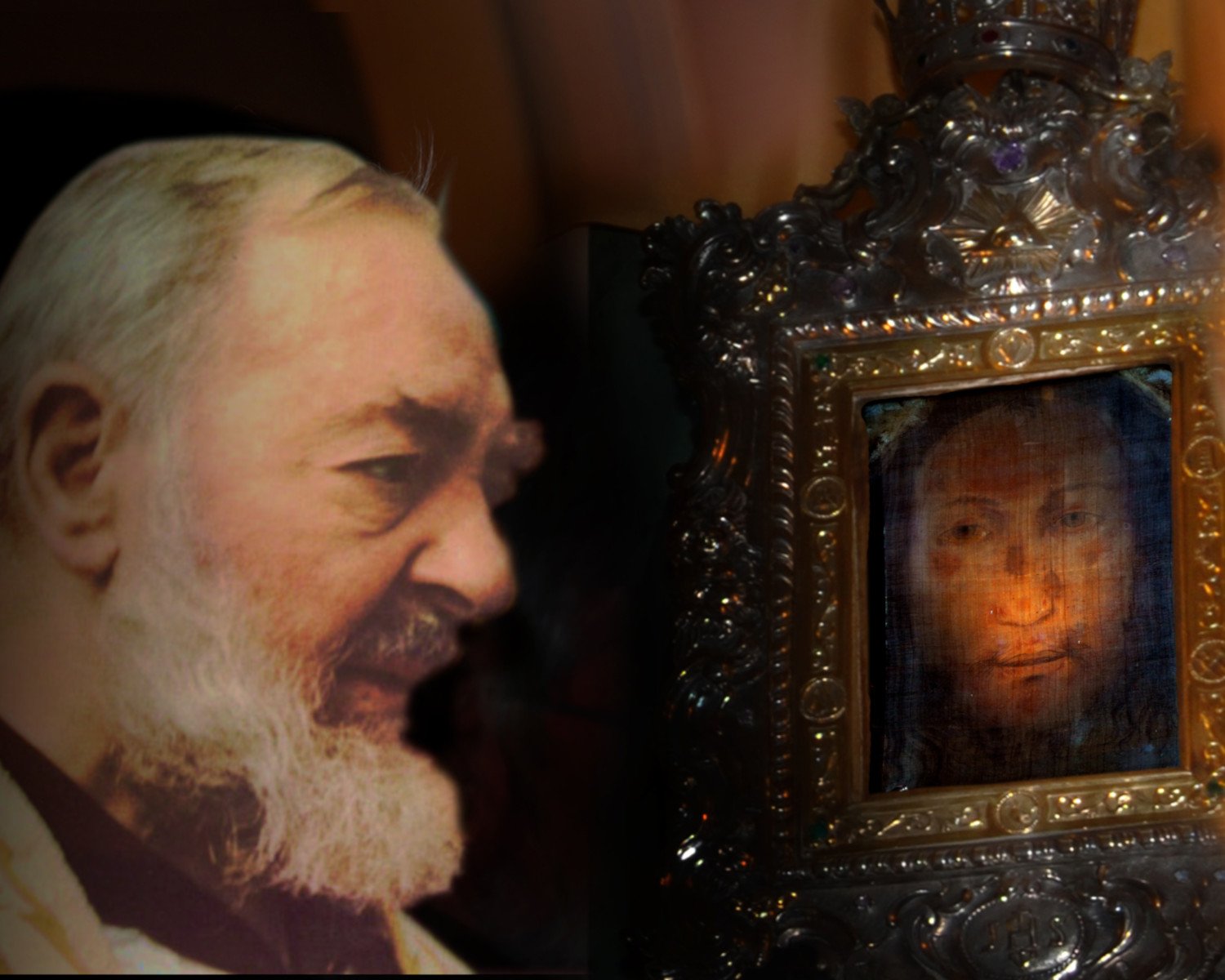
In the August-September 2012 issue of Inside the Vatican magazine, Australian journalist Paul MacLeod has a fascinating article reviewing two books by Paul Badde, The Face of God (Ignatius Press 2010) and The True Icon (Ignatius Press 2012). The two books “read like detective stories,” MacLeod wrote, as they examine in great depth two of the Church’s most revered treasures, the Shroud of Turin and the “Volto Santo,” the image of the Holy Face hidden for 400 years and believed to be the second burial cloth of Jesus, the sudarium.
The origin of the veil can be one of two sources, or a combination of both. Though the story never appears in Sacred Scripture, there is an ancient legend that a woman offered her head-cloth to wipe the face of Jesus on the way to Golgotha. When he gave it back to her, as the story has it, an impression of his face remained on the veil. What is now the Sixth Station of the Cross was legendary in Rome since the 8th Century. The name tradition has given to that woman is Veronica, a name that appears nowhere in the Gospel narrative of the Passion of Christ. The name comes from “Vera Icon,” Latin for “True Image,” a great treasure of the Church now preserved at the Shrine of the Holy Face at Manoppello in the Abruzzi region of Italy.
The veil is believed to be one of two burial cloths of Jesus, though it’s possible that both accounts are behind this treasure. On the morning of the resurrection, the Gospel of John (20:7) reports, the smaller burial cloth of Jesus — the veil covering his face — was rolled up in a place by itself as witnessed by Saint Peter and Saint John. In Jewish custom in the time of Jesus, such a veil covered the faces of dignitaries, such as the high priest, in death before being entombed. It is this veil that many now believe is enshrined at Manoppello. In contrast to that other, larger burial cloth — believed by many to be the Shroud of Turin — the image on the veil is not that of a dead man, however, but of a man very much alive, his eyes wide open. It is Jesus the Christ, having conquered death. In Inside the Vatican, Paul MacLeod described the Veil of Manoppello as:
“. . . a delicate, transparent piece of expensive material, measuring just 28 cm by 17 cm, in which the face of Jesus seems to float in light, even to store light.”
Paul MacLeod reported in the article that Capuchin priest, Father Domenico de Cese, formerly custodian of the shrine, was killed in an accident while visiting the Shroud of Turin in 1978. A decade earlier, however, Father Domenico wrote of a rather strange occurrence. On the morning of September 22, 1968, Father Domenico opened the doors of the shrine, and was startled to find Padre Pio kneeling in prayer before the image of the Holy Face. Padre Pio was at the same time 200 kilometers away at San Giovanni Rotondo, gravely ill, and near death.
“With My Body or Without It”
It was his last known occurrence of bilocation, a phenomenon that, like his visible wounds, became a source of skepticism about Padre Pio both in and outside of the Church. At 2:30 AM on the next morning — September 23, 1968 — Padre Pio died.
The two stories placed together — Padre Pio’s death and his prayer before the Veil of Manoppello — make perfect sense to me. In the hours before his death, Padre Pio contemplated the burial cloth of Christ. After fifty years of bearing the visible wounds of Christ, Padre Pio’s own soul sought out this visible link to Jesus beyond death; not Jesus crucified — a reality Padre Pio himself had lived for fifty years — but the image of the face of the risen Christ.
Padre Pio seemed most hesitant to discuss either his wounds or the reported incidents of bilocation. He seemed hesitant because in life he did not understand them at all. In fact, a Vatican investigator learned that all the events of bilocation were reported by others, and never by Padre Pio himself. It wasn’t until he was directly asked by the investigator that he described bilocation:
“I don’t know how it is or the nature of this phenomenon — and I certainly don’t give it much thought — but it did happen to me to be in the presence of this or that person, to be in this or that place; but I do not know whether I was there with my body or without it . . . Usually it has happened while I was praying . . . This is the first time I talk about this.”
— Padre Pio Under Investigation, Ignatius Press, 2008, p. 208
Those September days preceding Padre Pio’s death in 1968 must have been the strangest of his life. The visible wounds became so central to his sense of self for a half century that I imagine he had difficulty even remembering a time when the wounds were not present. Even a great burden carried for years upon years — I have learned the hard way — can become a part of who and what we are. We cannot imagine Padre Pio without these wounds. We would have never even heard of Padre Pio without these wounds. So in that sense, the wounds were not for him. They were for us.
But in the days before Padre Pio died, the wounds on his hands and feet and in his side began to close. He received those wounds on the morning of September 20, 1918. Fifty years later, on September 20, 1968, after a few days of the wounds slowly diminishing, all traces of them were gone. The wounds were then only within Padre Pio. Visible or not, they were a part of his very self.
In a previous post about Padre Pio I wrote of the day those wounds were given to him. I told the story of how this saint among us struggled with what had happened to him, and the lifelong trials that were set in motion by those visible wounds. It is a moving account of the Stigmata in Padre Pio’s own words in a letter to his Capuchin spiritual advisor, Padre Benedeto, a month after receiving the wounds.
“On the morning of the 20th of last month, in the choir, after I had celebrated Mass . . . I saw before me a mysterious person similar to the one I had seen on the evening of 5 August. The only difference was that his hands and feet and side were dripping blood. The sight terrified me and what I felt at that moment is indescribable. I thought I should die and really should have died if the Lord had not intervened and strengthened my heart which was about to burst out of my chest.
“The vision disappeared and I became aware that my hands and feet and side were dripping blood. Imagine the agony I experienced and continue to experience almost every day. The heart wound bleeds continually, especially from Thursday evening until Saturday.
“Dear Father, I am dying of pain because of the wounds and the resulting embarrassment I feel in my soul. I am afraid I shall bleed to death if the Lord does not hear my heartfelt supplication to relieve me of this condition.
“Will Jesus, who is so good, grant me this grace? Will he at least free me from the embarrassment caused by these outward signs? I will raise my voice and will not stop imploring him until in his mercy he takes away . . . these outward signs which cause me such embarrassment and unbearable humiliation.”
— Letters 1, No. 511
But it was the stories of bilocation that caused so much skeptical doubt. In May of 1921, the Vatican commenced its first of several investigations into Padre Pio’s life. The investigator, Monsignor Raffaelo Carlo Rossi, tried to refuse the assignment because he admittedly went into it with a “prejudice against Padre Pio.” After months of interrogations, depositions, interviews with other friars, and testimony by many laypeople, Bishop Rossi’s file was ordered sealed, and it remained sealed as a secret Vatican file for decades. The investigator concluded his file: “The future will reveal what today cannot be read in the life of Padre Pio of Pietrelcina.”
That investigator, we now know, left San Giovanni Rotondo with no doubt whatsoever about the true nature of Padre Pio, but it wasn’t enough to curtail years of further suspicion and persecution from within the Church. The story of Padre Pio’s treatment is best summed up by Father Paolo Rossi, former Postulator General of the Capuchin Order, and it seems a bit familiar:
“People would better understand the virtue of the man if they knew the degree of hostility he experienced from the Church… The Order itself was told to act in a certain way toward Padre Pio. So the hostility went all the way up to the Holy Office and the Vatican Secretariat of State. Faulty information was being given to Church authorities, and they acted on that information.”
— Making Saints, Simon and Schuster, 1990 p. 188
A Face on My Wall
If you look at the end of the “About” page at Beyond These Stone Walls, you may notice that this blog is published under the patronage of Saint Maximilian Kolbe and Saint Padre Pio, champions of truth, justice, and fidelity to the Risen Lord. The impact of Saint Maximilian on these prison walls is easy to see. How Saint Padre Pio insinuated himself here is a bit more mysterious.
It started with an awareness that we share an important date. The day I was convicted and taken to prison was September 23, Saint Padre Pio’s feast day and the last day of his earthly life. Only 26 years passed between those two events. Padre Pio just showed up here again, but that story needs a little background.
Despite its small size, the typical prison cell can seem a barren place. Like every prison this one has rows upon rows of cells, tiers upon tiers of them, all perfectly uniform, none with any evidence of human individualism. The whole point of prison is that its inhabitants are forced to view themselves as humans in degraded form, living a day to day existence that is entirely uniform, and devoid of any sense of the self.
The inside of these 6-by-10-foot walled and barred cells is composed of nothing but concrete. The four walls, the floor and the ceiling are bare concrete. The bunks upon which we sleep are concrete (and they hurt if I sleep too long), and so is the small counter upon which this prisoner is writing at this moment. Prison cells are distinguishable from other prison cells solely by the number above each solid steel door.
There is one small exception to the absence of human evidence, and I’ve written of it before. In “Angelic Justice: Saint Michael the Archangel and the Scales of Hesed,” I described the sole evidence of individualism in a prison cell. There are two rectangles, exactly 24 inches by 36 inches, painted on one wall with 12 inches of space in between them. Within these dark green rectangles, the two prisoners living in each cell may post a calendar, photos of their families and friends, and religious items. Nothing else.
You can learn a lot about a man from what is posted within this rectangle on his cell wall. In my first years in prison, commencing 28 years ago, I had lots of photos of family and friends, evidence of the life I once knew beyond these stone walls. Like every prisoner over time, that evidence slowly diminished. In my first five years in prison, I was moved 17 times, often with just minutes notice. Each time, I would take down all my evidence of a life, and then put it back on the wall in another cell on another tier in another building with other people. Each time, something of myself would be lost forever. Then the day came that I was moved, and nothing went back up onto the wall. The wall remained an empty space for many years.
This was true of my friend, Pornchai Moontri, as well. After 21 years in prison, beginning when he was barely 18 years old, Pornchai only vaguely recalls a life beyond and the people in it, but he no longer possesses any evidence of it. His uprootings were much more severe than mine. As you know from reading “Pornchai’s Story” he was ripped from a culture, a country, and a continent. Much was taken from him, and then, finally, so was his freedom. You know of that story which I wrote of in “Pornchai Moontri and the Long Road to Freedom.”
When we were moved to the same cell many years ago, Pornchai and I both stared each day at two green rectangles with nothing in them. Then Beyond These Stone Walls began a year later, and ever so slowly our wall became filled with images sent to us from readers. (Alas, such images are no longer allowed in mail, but the ones already on our wall can stay). Every square inch of Pornchai’s rectangle, even after he has left prison, is still filled with evidence of his very much alive Catholic faith.
But one day, I noticed that a very nice photograph of Saint Padre Pio that was in my rectangle on the wall somehow migrated over to Pornchai’s wall. On the day I noticed that my treasured image of Padre Pio “defected,” I also mentioned that I didn’t have another one and wished that someone would send me one. An hour after voicing that, the mail arrived. I opened an envelope from my friend, John Warwick, a reader in Pittsburgh.
I opened John’s envelope to find a beautiful card enrolling me and my intentions in a novena to Saint Padre Pio, and the image on the card was the very same one that took up residence over on Pornchai’s wall. It is my first experience of this great Patron Saint’s bilocation, and I treasure it. Thank you, John!
“Stay with me, Lord, for it is getting late: the day is ending, life is passing; death, judgment, eternity are coming soon … I have great need of you on this journey. It is getting late and death is approaching. Darkness, temptations, crosses and troubles beset me in this night of exile.”
— Saint Padre Pio’s Communion Prayer
+ + +
In the Absence of Fathers: A Story of Elephants and Men
Are committed fathers an endangered species in our culture? Fr. Gordon MacRae draws a troubling corollary between absent fathers and burgeoning prisons.
Are committed fathers an endangered species in our culture? Fr. Gordon MacRae draws a troubling corollary between absent fathers and burgeoning prisons.
Wade Horn, Ph.D., President of the National Fatherhood Initiative, had an intriguing article entitled “Of Elephants and Men” in a recent issue of Fatherhood Today magazine. I found Dr. Horn’s story about young elephants to be simply fascinating, and you will too. It was sent to me by a reader who wanted to know if there is any connection between the absence of fathers and the shocking growth of the American prison population.
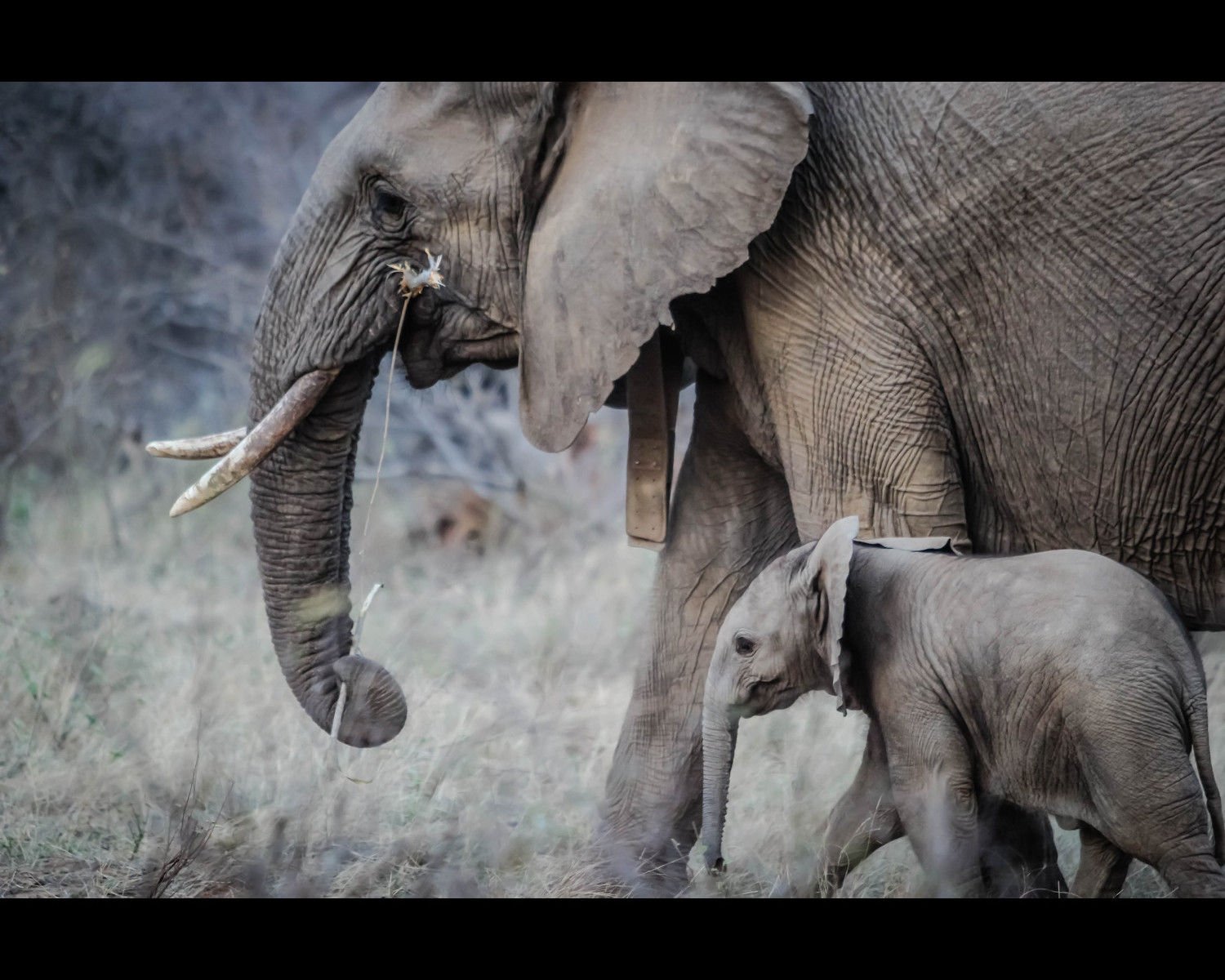
Some years ago, officials at the Kruger National Park and game reserve in South Africa were faced with a growing elephant problem. The population of African elephants, once endangered, had grown larger than the park could sustain. So measures had to be taken to thin the ranks. A plan was devised to relocate some of the elephants to other African game reserves. Being enormous creatures, elephants are not easily transported. So a special harness was created to air-lift the elephants and fly them out of the park using helicopters.
The helicopters were up to the task, but, as it turned out, the harness wasn’t. It could handle the juvenile and adult female elephants, but not the huge African bull elephants. A quick solution had to be found, so a decision was made to leave the much larger bulls at Kruger and relocate only some of the female elephants and juvenile males.
The problem was solved. The herd was thinned out, and all was well at Kruger National Park. Sometime later, however, a strange problem surfaced at South Africa’s other game reserve, Pilanesburg National Park, the younger elephants’ new home.
Rangers at Pilanesburg began finding the dead bodies of endangered white rhinoceros. At first, poachers were suspected, but the huge rhinos had not died of gunshot wounds, and their precious horns were left intact. The rhinos appeared to be killed violently, with deep puncture wounds. Not much in the wild can kill a rhino, so rangers set up hidden cameras throughout the park.
The result was shocking. The culprits turned out to be marauding bands of aggressive juvenile male elephants, the very elephants relocated from Kruger National Park a few years earlier. The young males were caught on camera chasing down the rhinos, knocking them over, and stomping and goring them to death with their tusks. The juvenile elephants were terrorizing other animals in the park as well. Such behavior was very rare among elephants. Something had gone terribly wrong.
Some of the park rangers settled on a theory. What had been missing from the relocated herd was the presence of the large dominant bulls that remained at Kruger. In natural circumstances, the adult bulls provide modeling behaviors for younger elephants, keeping them in line.
Juvenile male elephants, Dr. Horn pointed out, experience “musth,” a state of frenzy triggered by mating season and increases in testosterone. Normally, dominant bulls manage and contain the testosterone-induced frenzy in the younger males. Left without elephant modeling, the rangers theorized, the younger elephants were missing the civilizing influence of their elders as nature and pachyderm protocol intended.
To test the theory, the rangers constructed a bigger and stronger harness, then flew in some of the older bulls left behind at Kruger. Within weeks, the bizarre and violent behavior of the juvenile elephants stopped completely. The older bulls let them know that their behaviors were not elephant-like at all. In a short time, the younger elephants were following the older and more dominant bulls around while learning how to be elephants.
Marauding in Central Park
In his terrific article, “Of Elephants and Men,” Dr. Wade Horn went on to write of a story very similar to that of the elephants, though it happened not in Africa, but in New York’s Central Park. The story involved young men, not young elephants, but the details were eerily close. Groups of young men were caught on camera sexually harassing and robbing women and victimizing others in the park. Their herd mentality created a sort of frenzy that was both brazen and contagious. In broad daylight, they seemed to compete with each other, even laughing and mugging for the cameras as they assaulted and robbed passersby. It was not, in any sense of the term, the behavior of civilized men.
Appalled by these assaults, citizens demanded a stronger and more aggressive police presence. Dr. Horn asked a more probing question. “Where have all the fathers gone?” Simply increasing the presence of police everywhere a crime is possible might assuage some political pressure, but it does little to identify and solve the real social problem behind the brazen Central Park assaults. It was the very same problem that victimized rhinos in that park in Africa. The majority of the young men hanging around committing those crimes in Central Park grew up in homes without fathers present.
That is not an excuse. It is a social problem that has a direct correlation with their criminal behavior. They were not acting like men because their only experience of modeling the behaviors of men had been taught by their peers and not by their fathers. Those who did have fathers had absent fathers, clearly preoccupied with something other than being role models for their sons. Wherever those fathers were, they were not in Central Park.
Dr. Horn pointed out that simply replacing fathers with more police isn’t a solution. No matter how many police are hired and trained, they will quickly be outnumbered if they assume the task of both investigating crime and preventing crime. They will quickly be outnumbered because presently in our culture, two out of every five young men are raised in fatherless homes, and that disparity is growing faster as traditional family systems break down throughout the Western world.
Real men protect the vulnerable. They do not assault them. Growing up having learned that most basic tenet of manhood is the job of fathers, not the police. Dr. Horn cited a quote from a young Daniel Patrick Moynihan written some forty years ago:
“From the wild Irish slums of the 19th Century Eastern Seaboard to the riot-torn suburbs of Los Angeles, there is one unmistakable lesson in American history: A community that allows a large number of young men to grow up in broken homes, dominated by women, never acquiring any stable relationship to male authority, never acquiring any rational expectations for the future — that community asks for and gets chaos.”
When Prisons Replace Parents
It’s easy in the politically correct standards of today to dismiss such a quote as chauvinistic. But while we’re arguing that point, our society’s young men are being tossed away by the thousands into prison systems that swallow them up. Once in prison, this system is very hard to leave behind. The New Hampshire prison system just released a dismal report two weeks ago. Of 1,095 prisoners released in 2007, over 500 were back in prison by 2010. Clearly, the loss of freedom does not compensate for the loss of fathers in managing the behavior of young men.
There is very little that happens in the punishment model of prison life that teaches a better way to a young man who has broken the law. The proof of that is all around us, but — especially in an election year — getting anyone to take a good hard look inside a prison seems impossible. We live in a disposable culture, and when our youth are a problem, we simply do what we do best. We dispose of them, sometimes forever. Anyone who believes that punishment, and nothing but punishment, is an effective deterrent of criminal behavior in the young is left to explain why our grotesquely expensive prisons have a 50 percent recidivism rate.
As I have written before, the United States has less than five percent of the world’s population, but twenty-five percent of the world’s prisoners. The U.S. has more young men in prison today than all of the leading 35 European countries combined. The ratio of prisoners to citizens in the U.S. is four times what it is in Israel, six times what it is in Canada and China, and thirteen times what it is in Japan. The only governments with higher per capita rates of prisoners are in Third World countries, and even they are only slightly higher.
For a nation struggling with its racial inequities, the prison system is a racial disaster. Currently, young men of African-American and Latino descent comprise 30 percent of our population, but 60 percent of our prison population. But prison isn’t itself an issue that falls conveniently along racial divides.
New Hampshire, where I have spent the last twenty-six years in prison, is one of the whitest states in the United States, and yet it is first in the nation not only in its Presidential Primary election, but in prison growth relative to population growth. Between 1980 and 2005, New Hampshire’s state population grew by 34 percent. In that same period, its prison population grew by a staggering 600 percent with no commensurate increase in crime rate.
In an election year, politicizing prisons is just counter-productive and nothing will ever really change. Albert R. Hunt of Bloomberg News had a recent op-ed piece in The New York Times (“A Country of Inmates,” November 20, 2011) in which he decried the election year politics of prisons.
“This issue [of prison growth] almost never comes up with Republican presidential candidates; one of the few exceptions was a debate in September when audiences cheered the notion of executions in Texas.”
This may be so, but it’s the very sort of political blaming that undermines real serious and objective study of our national prison problem. I am not a Republican or a Democrat, but in fairness I should point out that the recent Democratic governor of New Hampshire had but one plan for this State’s overcrowded and ever growing prison system: build a bigger prison somewhere. And as far as executions are concerned, the overwhelmingly Republican state Legislature in New Hampshire voted overwhelmingly to overturn the state’s death penalty ten years ago. Governor Jeanne Shaheen (now U.S. Senator Jeanne Shaheen), a Democrat, vetoed the repeal saying that this State “needs a death penalty.” (In 2020, the death penalty was finally rescinded in New Hampshire.)
More dismal still, New Hampshire is also first in the nation in deaths of young men between the ages of 16 and 34. This is largely attributed to opiates addiction and all the hopelessness it entails. Young men growing up in fatherless homes are exponentially more likely than any others to fall prey to addiction.
Eighty percent of the young men I have met in prison grew up in homes without fathers. The problem seems clear. When prisons and police replace fathers, chaos reigns, and promising young lives are sacrificed.
Before we close the door on Father’s Day this year, let’s revisit whether we’re prepared for the chaos of a fatherless America. “Fathers” and “Fatherhood” are concepts with 1,932 direct references in the Old and New Testaments. Without a doubt, fatherhood has long been on the mind of God.
+ + +
Don’t miss these related posts from Beyond These Stone Walls:
Please share this post!
Dismas, Crucified to the Right: Paradise Lost and Found
Who was Saint Dismas, the Penitent Thief, crucified to the right of Jesus at Calvary? His brief Passion Narrative appearance has deep meaning for Christians.
Who was Saint Dismas, the Penitent Thief, crucified to the right of Jesus at Calvary? His brief Passion Narrative appearance has deep meaning for Salvation.
“All who see me scoff at me. They mock me with parted lips; they wag their heads.”
During Holy Week one year, I wrote “Simon of Cyrene, the Scandal of the Cross, and Some Life Sight News.” It was about the man recruited by Roman soldiers to help carry the Cross of Christ. I have always been fascinated by Simon of Cyrene, but truth be told, I have no doubt that I would react with his same spontaneous revulsion if fate had me walking in his sandals that day past Mount Calvary.
Some BTSW readers might wish for a different version, but I cannot write that I would have heroically thrust the Cross of Christ upon my own back. Please rid yourselves of any such delusion. Like most of you, I have had to be dragged kicking and screaming into just about every grace I have ever endured. The only hero at Calvary was Christ. The only person worth following up that hill — up ANY hill — is Christ. I follow Him with the same burdens and trepidation and thorns in my side as you do. So don’t follow me. Follow Him.
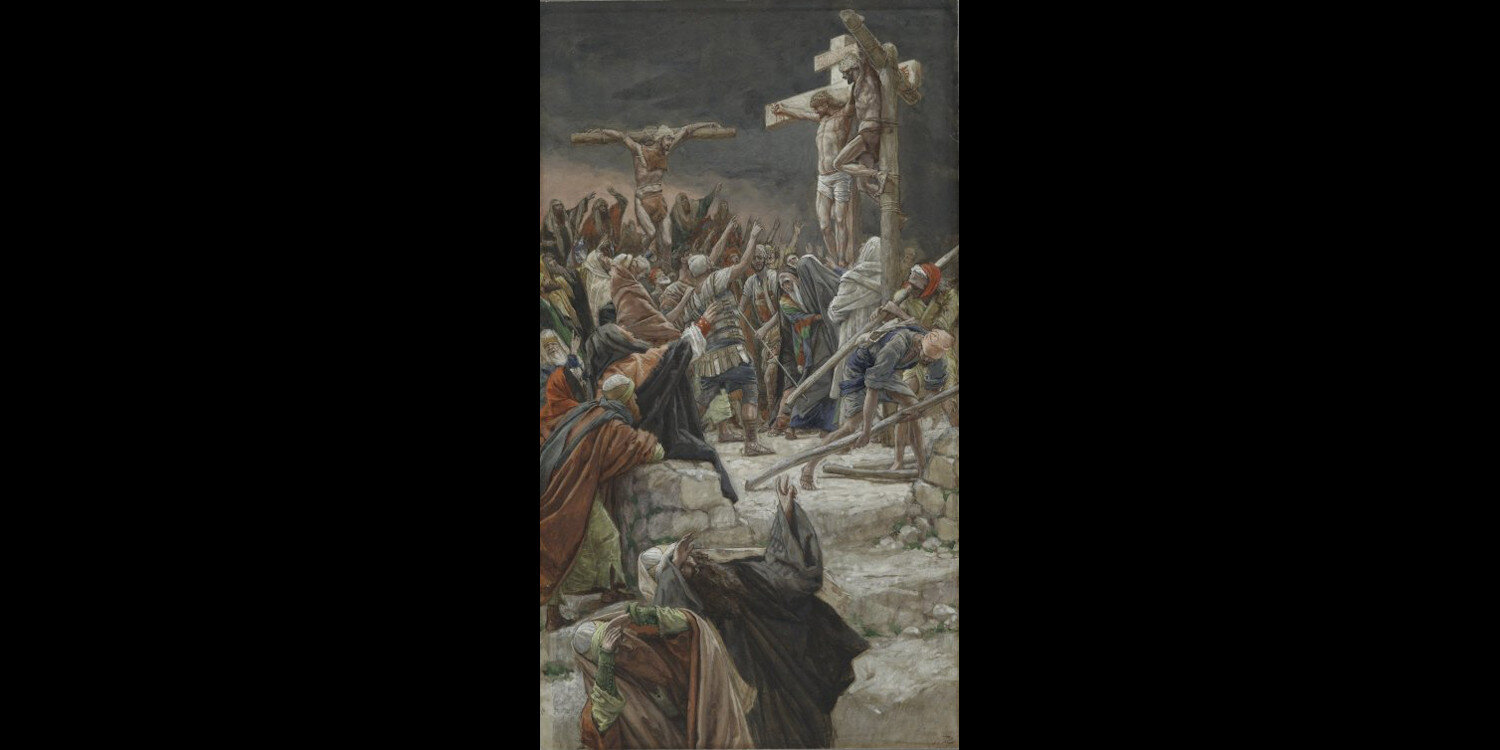
This Holy Week, one of many behind these stone walls, has caused me to use a wider angle lens as I examine the events of that day on Mount Calvary as the Evangelists described them. This year, it is Dismas who stands out. Dismas is the name tradition gives to the man crucified to the right of the Lord, and upon whom is bestowed a dubious title: the “Good Thief.”
As I pondered the plight of Dismas at Calvary, my mind rolled some old footage, an instant replay of the day I was sent to prison — the day I felt the least priestly of all the days of my priesthood.
It was the mocking that was the worst. Upon my arrival at prison after trial late in 1994, I was fingerprinted, photographed, stripped naked, showered, and unceremoniously deloused. I didn’t bother worrying about what the food might be like, or whether I could ever sleep in such a place. I was worried only about being mocked, but there was no escaping it. As I was led from place to place in chains and restraints, my few belongings and bedding stuffed into a plastic trash bag dragged along behind me, I was greeted by a foot-stomping chant of prisoners prepped for my arrival: “Kill the priest! Kill the priest! Kill the priest!” It went on into the night. It was maddening.
It’s odd that I also remember being conscious, on that first day, of the plight of the two prisoners who had the misfortune of being sentenced on the same day I was. They are long gone now, sentenced back then to just a few years in prison. But I remember the walk from the courthouse in Keene, New Hampshire to a prison-bound van, being led in chains and restraints on the “perp-walk” past rolling news cameras. A microphone was shoved in my face: “Did you do it, Father? Are you guilty?”
You may have even witnessed some of that scene as the news footage was recently hauled out of mothballs for a WMUR-TV news clip about my new appeal. Quickly led toward the van back then, I tripped on the first step and started to fall, but the strong hands of two guards on my chains dragged me to my feet again. I climbed into the van, into an empty middle seat, and felt a pang of sorrow for the other two convicted criminals — one in the seat in front of me, and the other behind.
“Just my %¢$#@*& luck!” the one in front scowled as the cameras snapped a few shots through the van windows. I heard a groan from the one behind as he realized he might vicariously make the evening news. “No talking!” barked a guard as the van rolled off for the 90 minute ride to prison. I never saw those two men again, but as we were led through the prison door, the one behind me muttered something barely audible: “Be strong, Father.”
Revolutionary Outlaws
It was the last gesture of consolation I would hear for a long, long time. It was the last time I heard my priesthood referred to with anything but contempt for years to come. Still, to this very day, it is not Christ with whom I identify at Calvary, but Simon of Cyrene. As I wrote in “Simon of Cyrene and the Scandal of the Cross“:
“That man, Simon, is me . . . I have tried to be an Alter Christus, as priesthood requires, but on our shared road to Calvary, I relate far more to Simon of Cyrene. I pick up my own crosses reluctantly, with resentment at first, and I have to walk behind Christ for a long, long time before anything in me compels me to carry willingly what fate has saddled me with . . . I long ago had to settle for emulating Simon of Cyrene, compelled to bear the Cross in Christ’s shadow.”
So though we never hear from Simon of Cyrene again once his deed is done, I’m going to imagine that he remained there. He must have, really. How could he have willingly left? I’m going to imagine that he remained there and heard the exchange between Christ and the criminals crucified to His left and His right, and took comfort in what he heard. I heard Dismas in the young man who whispered “Be strong, Father.” But I heard him with the ears of Simon of Cyrene.
Like a Thief in the Night
Like the Magi I wrote of in “Upon a Midnight Not So Clear,” the name tradition gives to the Penitent Thief appears nowhere in Sacred Scripture. Dismas is named in a Fourth Century apocryphal manuscript called the “Acts of Pilate.” The text is similar to, and likely borrowed from, Saint Luke’s Gospel:
“And one of the robbers who were hanged, by name Gestas, said to him: ‘If you are the Christ, free yourself and us.’ And Dismas rebuked him, saying: ‘Do you not even fear God, who is in this condemnation? For we justly and deservedly received these things we endure, but he has done no evil.’”
What the Evangelists tell us of those crucified with Christ is limited. In Saint Matthew’s Gospel (27:38) the two men are simply “thieves.” In Saint Mark’s Gospel (15:27), they are also thieves, and all four Gospels describe their being crucified “one on the left and one on the right” of Jesus. Saint Mark also links them to Barabbas, guilty of murder and insurrection. The Gospel of Saint John does the same, but also identifies Barabbas as a robber. The Greek word used to identify the two thieves crucified with Jesus is a broader term than just “thief.” Its meaning would be more akin to “plunderer,” part of a roving band caught and given a death penalty under Roman law.
Only Saint Luke’s Gospel infers that the two thieves might have been a part of the Way of the Cross in which Saint Luke includes others: Simon of Cyrene carrying Jesus’ cross, and some women with whom Jesus spoke along the way. We are left to wonder what the two criminals witnessed, what interaction Simon of Cyrene might have had with them, and what they deduced from Simon being drafted to help carry the Cross of a scourged and vilified Christ.
In all of the Gospel presentations of events at Golgotha, Jesus was mocked. It is likely that he was at first mocked by both men to be crucified with him as the Gospel of St. Mark describes. But Saint Luke carefully portrays the change of heart within Dismas in his own final hour. The sense is that Dismas had no quibble with the Roman justice that had befallen him. It seems no more than what he always expected if caught:
“One of the criminals who were hanged railed at him, saying, ‘Are you not the Christ? Save yourself and us!’ But the other rebuked him, saying, ‘Do you not fear God since you are under the same sentence of condemnation? And we indeed justly, for we are receiving the due reward of our deeds; but this man has done nothing wrong.’ ”
The Flight into Egypt
The name, “Dismas” comes from the Greek for either “sunset” or “death.” In an unsubstantiated legend that circulated in the Middle Ages, in a document known as the “Arabic Gospel of the Infancy,” this encounter from atop Calvary was not the first Gestas and Dismas had with Jesus. In the legend, they were a part of a band of robbers who held up the Holy Family during the Flight into Egypt after the Magi departed in Saint Matthews Gospel (Matthew 2:13-15).
This legendary encounter in the Egyptian desert is also mentioned by Saint Augustine and Saint John Chrysostom who, having heard the same legend, described Dismas as a desert nomad, guilty of many crimes including the crime of fratricide, the murder of his own brother. This particular part of the legend, as you will see below, may have great symbolic meaning for salvation history.
In the legend, Saint Joseph, warned away from Herod by an angel (Matthew 2:13-15), opted for the danger posed by brigands over the danger posed by Herod’s pursuit. Fleeing with Mary and the child into the desert toward Egypt, they were confronted by a band of robbers led by Gestas and a young Dismas. The Holy Family looked like an unlikely target having fled in a hurry, and with very few possessions. When the robbers searched them, however, they were astonished to find expensive gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh — the Gifts of the Magi. However, in the legend Dismas was deeply affected by the infant, and stopped the robbery by offering a bribe to Gestas. Upon departing, the young Dismas was reported to have said:
“0 most blessed of children, if ever a time should come when I should crave thy mercy, remember me and forget not what has passed this day.”
Paradise Found
The most fascinating part of the exchange between Jesus and Dismas from their respective crosses in Saint Luke’s Gospel is an echo of that legendary exchange in the desert 33 years earlier — or perhaps the other way around:
“‘Jesus, remember me when you come into your kingly power.’ And he said to him, ‘Truly I say to you, today you will be with me in Paradise.’”
The word, “Paradise” used by Saint Luke is the Persian word, “Paradeisos” rarely used in Greek. It appears only three times in the New Testament. The first is that statement of Jesus to Dismas from the Cross in Luke 23:43. The second is in Saint Paul’s description of the place he was taken to momentarily in his conversion experience in Second Corinthians 12:3 — which I described in “The Conversion of Saint Paul and the Cost of Discipleship.” The third is the heavenly paradise that awaits the souls of the just in the Book of Revelation (2:7).
In the Old Testament, the word “Paradeisos” appears only in descriptions of the Garden of Eden in Genesis 2:8, and in the banishment of Cain after the murder of his brother, Abel:
“Cain left the presence of the Lord and wandered in the Land of Nod, East of Eden.”
Elsewhere, the word appears only in the prophets (Isaiah 51:3 and Ezekiel 36:35) as they foretold a messianic return one day to the blissful conditions of Eden — to the condition restored when God issues a pardon to man.
If the Genesis story of Cain being banished to wander “In the Land of Nod, East of Eden” is the symbolic beginning of our human alienation from God — the banishment from Eden marking an end to the State of Grace and Paradise Lost — then the Dismas profession of faith in Christ’s mercy is symbolic of Eden restored — Paradise Regained.
From the Cross, Jesus promised Dismas both a return to spiritual Eden and a restoration of the condition of spiritual adoption that existed before the Fall of Man. It’s easy to see why legends spread by the Church Fathers involved Dismas guilty of the crime of fratricide just as was Cain.
A portion of the cross upon which Dismas is said to have died alongside Christ is preserved at the Church of Santa Croce in Rome. It’s one of the Church’s most treasured relics. Catholic apologist, Jim Blackburn has proposed an intriguing twist on the exchange on the Cross between Christ and Saint Dismas. In “Dismissing the Dismas Case,” an article in the superb Catholic Answers Magazine Jim Blackburn reminded me that the Greek in which Saint Luke’s Gospel was written contains no punctuation. Punctuation had to be added in translation. Traditionally, we understand Christ’s statement to the man on the cross to his right to be:
“Truly I say to you, today you will be with me in Paradise.”
The sentence has been used by some non-Catholics (and a few Catholics) to discount a Scriptural basis for Purgatory. How could Purgatory be as necessary as I described it to be in “The Holy Longing” when even a notorious criminal is given immediate admission to Paradise? Ever the insightful thinker, Jim Blackburn proposed a simple replacement of the comma giving the verse an entirely different meaning:
“Truly I say to you today, you will be with me in Paradise.”
Whatever the timeline, the essential point could not be clearer. The door to Divine Mercy was opened by the events of that day, and the man crucified to the right of the Lord, by a simple act of faith and repentance and reliance on Divine Mercy, was shown a glimpse of Paradise Regained.
The gift of Paradise Regained left the cross of Dismas on Mount Calvary. It leaves all of our crosses there. Just as Cain set in motion our wandering “In the Land of Nod, East of Eden,” Dismas was given a new view from his cross, a view beyond death, away from the East of Eden, across the Undiscovered Country, toward eternal home.
Saint Dismas, pray for us.
+ + +
Upon a Midnight Not So Clear, Some Wise Men from the East Appear
There is a back story to the Magi of Saint Matthew's account of the Birth of Christ, and it is the Gospel for the Epiphany of the Lord.
There’s a back story to the Magi of Saint Matthew’s account of the Birth of Christ, and it is the Gospel for the Epiphany of the Lord.
In early December each year, prisoners here can purchase a 20-lb food package from a vendor. They drop hints to their families, and those without families scrape and save their meager prison pay all year. No one here wants to pass up a chance to purchase food they otherwise won’t see again until next year. Most are practical about it. They skip the candy and cookies to buy more sustaining items like real coffee, and meal alternatives they can save for the worst days in the prison chow hall.
The packages arrived last week, and for days prisoners have been bringing me samples of their culinary creations. They come to my cell door with an endless parade of sandwiches, wraps, and pizzas. I learned long ago that refusing the food leaves a lot of hurt feelings. They not only insist that I eat it, but they insist on staying until I declare that their culinary skill surpasses all others. It’s beginning to look a lot like Christmas when I have to struggle into my pants in the morning.
There’s a point to these visits. Prisoners tell me about their own back stories, and the prospect of another Christmas in prison. They want to hear that they are not without hope. Most of all, they want to know that Christmas means more than the empty, shallow “holiday season” it has become on TV.
But this morning, my Japanese friend, Koji, stopped by with some coffee he brewed using an old sock. (Trust me, you don’t want the gory details!). Koji handed me a cup — it’s pretty good, actually — and asked, “What can you tell me about the Magi?” That was odd because I’ve been thinking of writing about the Magi for Christmas. I told Koji I’ll let him read this post when finished. Maybe he’ll bring me more coffee made with that old sock of his. Lord, give me the strength to bear my blessings! Anyway, there’s no better place to begin the Magi story than St. Matthew’s own words:
“Now when Jesus was born in Bethlehem of Judea in the days of Herod the king, behold, wise men from the East came to Jerusalem, saying, ‘Where is he who has been born king of the Jews? For we have seen his star in the East, and have come to worship him.’ When Herod the king heard this, he was troubled, and all Jerusalem with him; and assembling all the chief priests and scribes of the people, he inquired of them where the Christ was to be born. They told him, ‘In Bethlehem of Judea; for so it is written by the prophet:
‘And you, 0 Bethlehem, in the land of Judah, are by no means least among the rulers of Judah; for from you shall come a ruler who will govern my people, Israel.’
Then Herod summoned the wise men secretly and ascertained from them what time the star had appeared; and he sent them to Bethlehem, saying, ‘Go and search diligently for the child, and when you have found him bring me word, that I too may come and worship him.’ When they had heard the king, they went their way; and lo, the star which they had seen in the East went before them, till it came to rest over the place where the child was. When they saw the star, they rejoiced exceedingly with great joy; and going into the house they saw the child with Mary his mother, and they fell down and worshipped him. Then, opening their treasures, they offered him gifts, gold, frankincense and myrrh. And being warned in a dream not to return to Herod, they departed to their own country by another way.”
Myth, Midrash, or Both?
This story, as Saint Matthew relates it, is a myth. But don’t get me wrong. That does not mean the story isn’t true. In fact, I firmly believe that it is true. The word, “myth,” coming from the Greek “mythos,” simply means “story,” and makes no judgement on whether a story is historical. Myth is not synonymous with falsehood despite how its more modern meaning has been twisted into such a conclusion. In theology and Biblical studies, myth simply denotes a story imbued with rich theological and symbolic meaning, but that does not mean it’s devoid of historical truth.
Biblical myth is distinguished from legends and “folklore” by the way it offers explanations about the facts of a story. In myth, the explanations stand whether the facts stand or not, and the value of the story does not depend on its historical accuracy. Perhaps the best example is the Creation story of Genesis, Chapter 1. In my post, “A Day Without Yesterday,” the great Belgian physicist, Father Georges Lemaitre, turned modern cosmology on its head with his theory of the Big Bang. For Pope Pius XI, this proof of a universe that begins and ends in history affirmed the elemental truth of Biblical Creation.
When I say that the story of the Magi is true, however, I mean truth in both senses. The understanding the story conveys is the truth. The historical facts of the story are also the truth, and we have no reason to doubt them.
The account of the Magi is also a “midrash.” Midrash is a Hebrew term meaning “interpretation.” It’s a characteristic of many of the reflections in the Aggadah — which in Hebrew means “narrative.” The Aggadah is a collection of Rabbinic reflection and teaching gathered over a thousand years. Midrash is a type of literature from the Aggadah that interprets Biblical texts by linking them together and discerning their hidden meanings.
Like myth, midrash is not a declaration that a Biblical passage is not historical or true just because it contains elements of other Biblical texts. In Saint Matthew’s Gospel, the Magi story points to many elements in Old Testament Scriptures. Jewish Christians hearing Saint Matthew’s account of the Magi, for example, would connect the Star in the East witnessed by the Magi with the star Balaam (a sort of Magus figure) envisioned arising out of Jacob in a dream-like account described in the Book of Numbers 24:17. Herod’s affront with the idea of a Hebrew King in the Magi account echoes Balaam’s vision as well. Herod is of the Edomite clan. In Balaam’s vision, the star arising out of Jacob is a portent that “Edom shall be dispossessed.” (Numbers 24:18).
The account of wicked King Herod feeling threatened by the life of the infant Jesus recalls clearly the Exodus account of a wicked Pharaoh who, having enslaved the Jews, seeks the life of the infant Moses. And in the Infancy Narrative of Saint Luke’s Gospel, the story of Zechariah and Elizabeth conceiving a child in their old age is clearly an echo of the Genesis story of Abraham, Sarah, and Isaac.
In “Saint Gabriel the Archangel: When the Dawn from On High Broke Upon Us,” I wrote of how St. Luke drew many midrashic links with the Hebrew Scriptures in his account of the Angelic visit to Mary at the Annunciation. The account of Mary visiting Elizabeth in the hill country of Judea recalls David visiting the very same place to retrieve the Ark of the Covenant as told in 2 Samuel, Chapter 6. Even the story of the future John the Baptist leaping in his mother’s womb in the presence of Mary is midrashic. In 2 Samuel, David leaps for joy in the presence of the Ark of the Covenant. I find these echoes of the Old Testament to be fascinating, but they don’t leave the story’s historical truth in question, including the Magi story.
I have a modern analogy in my own family. I wrote about my father’s conversion in “What Do John Wayne and Pornchai Moontri Have in Common?” My father’s parents had four children. He grew up with two brothers and a sister. One of his brothers became a priest. A generation later, my father and mother had four children. I also grew up with two brothers and a sister. Both I and my father’s brother who became a priest were the second son in our families. Many of the stories of my own childhood have eerie echoes in my father’s childhood. This is what is meant by midrash.
The Epiphany is depicted in a mural titled “Adoration of the Magi” in the Basilica of the Immaculate Conception at Conception Abbey in Conception, MO. Painted by Benedictine monks in the late 1800s.
The Gifts of the Magi
There are elements within our popular understanding of the story of the Magi, however, that history has added over the centuries. For example, nothing in Saint Matthew’s account indicates that the Magi were three in number. The sole hint is in the number of their gifts: gold, frankincense, and myrrh. And despite the popular Christmas carol, “We Three Kings,” there is nothing in Saint Matthew’s account to indicate that they were kings. This account became linked to a passage in Isaiah:
“And nations shall come to your light, and kings to the brightness of your rising . . . they shall bring gold and frankincense, and shall proclaim the praise of the Lord.”
And linked as well was a passage about kings bringing tribute in Psalm 72:
“May the kings of Tarshish and of the isles render him tribute; may the kings of Sheba and Seba bring gifts”
Much theological symbolism for the gifts themselves was reflected upon later. Saint Ireneaus held that the Gifts of the Magi signify Christ Incarnate. Gold, a symbol of royalty, signifies Christ the King. Frankincense, used throughout ancient Israel in the worship of God, signifies divinity, and myrrh, an anointing oil for burial, signifies the Passion and death of the Messiah.
Saint Gregory the Great added to this interpretation with the Gifts of the Magi symbolizing our duty toward Christ in our daily lives. Gold signifies Christ’s wisdom and our deference. Frankincense signifies our prayer and adoration of Christ, and myrrh signifies our daily sacrifices as a share in the suffering of Christ. The names of the Magi — Gaspar, Melchior, and Balthazar — came out of a sixth century legend.
East of Eden
It’s widely held in Catholic scholarship that the Magi represent the first Gentiles to come to worship the Christ. There is one strain of scholarship that makes reference to the fact that they were astrologers who represented the world of magic. Most scholars see the Magi as followers of Zoroaster, an Indo-Iranian prophet who lived 12 centuries before Christ. Throughout the eastern world, followers of Zoroaster dominated religious thought for centuries. And yet there they are, kneeling in the presence of Christ. The symbolism is that as Christ reigns supreme, all other magic goes out of the world and loses its power and authority. It’s a beautiful and powerful image of the universal Kingship of Christ for all time, and the vast change his birth brought to the history of humankind.
I have an additional theory of my own about the hidden meaning of the account of the Magi, but I have been unable to find any reference to it in the work of any Biblical scholar, Catholic or otherwise. So I’m on my own in this wilderness of midrashic symbols. It’s true that the Magi represent all the world beyond Judaism coming into a covenant relationship with God through Christ. But great pains are taken by Saint Matthew to remind us repeatedly that the Magi are coming out of the East — and he capitalized “East.” It seems to me to be intended to designate more than just a compass point. The fact that they came from the East, and saw his star in the East, is repeated by Saint Matthew three times in this brief account.
In one of my posts on These Stone Walls — “In the Land of Nod, East of Eden” — I wrote of how both Adam and Eve were banished East of Eden after the Fall of Man (Genesis 3:24). It was both a punishment and a deterrent. God then placed a Cherubim with a flaming sword to the East of Eden to bar Man’s return.
A generation later, after the murder of his brother, Abel, Cain was also banished. Cain “went away from the presence of the Lord and dwelt in the Land of Nod, East of Eden (Genesis 4:14). The “Land of Nod” has no other reference in all of Scripture, and is widely interpreted to have its origin in the Hebrew term, “nad,” which means “to wander.” Cain himself described his fate in just this way:
“From thy face I shall be hidden; I shall be a fugitive and a wanderer on the earth.”
I count 21 references to an ill wind from the East throughout Sacred Scripture, but not one such reference after the Birth of Christ. An example is this one from the Prophet Isaiah:
“Measure by measure, by exile thou didst contend with them; he removed them with his fierce blast in the day of the east wind.”
For me, the Magi represent also those who have fallen, who have become alienated from God and banished East of Eden. They saw his star there, and followed its light. I am in a place filled with men who lived their entire lives East of Eden, and for them the Magi are a sign of Good News — the very best news. Freedom can be found in only one place: and the way there is the Star of Bethlehem.
Amid the Encircling Gloom
My cell window faces West so my gaze is always out of the East. On this cold and gray December day, the sun is just now setting behind the high prison wall, and glistening upon the spirals of razor wire like tinsel. Its final glimmer of light is just now fading from view. I am reminded of my favorite prayer, a gift from another wise man, Blessed John Henry Newman, and it has become a tradition of sorts as the Sun sets on These Stone Walls at Christmas. I can hear the Magi praying this as they follow that Star out of the East. On my 18th Christmas in prison, this is my prayer for you as well:
“Lead, kindly Light, amid the encircling gloom,
Lead Thou me on.
The night is dark, and I am far from home;
Lead Thou me on
Keep Thou my feet; I do not ask to see
The distant scene; One step enough for me.
I was not ever thus,
Nor prayed that Thou shouldst lead me on;
I loved to choose and see my path,
But now lead Thou me on.
I loved the garish day, and, spite of fears,
Pride ruled my will; remember not past years.
So long Thy power hath blessed me,
Sure it still will lead me on
O’er moor and fen, o’er crag and torrent
Till the night is gone,
And with the morn those Angel faces smile,
Which I have loved long since, and lost awhile.”
The readers of These Stone Walls have cast a light into the darkness and isolation of prison this year. It’s a light that illuminates the path from East of Eden, and it is magnified ever so brightly, in my life and in yours, by the Birth of Christ. The darkness can never, ever, ever overcome it.
+ + +
Please share this post!
What do John Wayne and Pornchai Moontri Have In Common?
As Advent begins in the midst of some long-awaited changes and revisions in the Catholic Mass, I have been doing some thinking about the nature of change.
As Advent begins in the midst of some long-awaited changes and revisions in the Catholic Mass, I have been doing some thinking about the nature of change.
In “February Tales,” an early post at Beyond These Stone Walls, I described growing up on the Massachusetts North Shore — the stretch of seacoast just north of Boston. My family had a long tradition of being “Sacrament Catholics.”
I once heard my father joke that he would enter a church only twice in his lifetime, and would be carried both times. I was seven years old, squirming into a hand-me-down white suit for my First Communion when I first heard that excuse for staying home. I didn’t catch on right away that my father was referring to his Baptism and his funeral. I pictured him, a very large man, slung over my mother’s shoulder on his way into church for Sunday Mass, and I laughed.
We were the most nominal of Catholics. Prior to my First Communion at age seven, I was last in a Catholic church at age five for the priesthood ordination of my uncle, the late Father George W. MacRae, a Jesuit and renowned Scripture scholar. My father and “Uncle Winsor,” as we called him, were brothers — just two years apart in age but light years apart in their experience of faith. I was often bewildered, as a boy, at this vast difference between the two brothers.
But my father’s blustering about his abstention from faith eventually collapsed under the weight of his own cross. It was a cross that was partly borne by me as well, and carried in equal measure by every member of my family. By the time I was ten — at the very start of that decade of social upheaval, life in our home had disintegrated. My father’s alcoholism raged beyond control, nearly destroying him and the very bonds of our family. We became children of the city streets as home and family faded away.
I have no doubt that many readers can relate to the story of a home torn asunder by alcoholism, and some day soon I plan to write much more about this cross. But for now I want to write about conversion, so I’ll skip ahead.
The Long and Winding Road Home
As a young teenager, I had a friend whose family attended a small Methodist church. I stayed with them from time to time. They knew I was estranged from my Catholic faith and Church, so one Sunday morning they invited me to theirs. As I sat through the Methodist service, I just felt empty inside. There was something crucial missing. So a week later, I attended Catholic Mass — secretly and alone — with a sense that I was making up for some vague betrayal. At some point sitting in this Mass alone at age 15, I discovered that I was home.
My father wasn’t far behind me. Two years later, when just about everyone we knew had given up any hope for him, my father underwent a radical conversion that changed his very core. He admitted himself to a treatment program, climbed the steep and arduous mountain of recovery, and became our father again after a long, turbulent absence. A high school dropout and machine shop laborer, my father’s transformation was miraculous. He went back to school, completed a college degree, earned his masters degree in social work, and became instrumental in transforming the lives of many other broken men. He also embraced his Catholic faith with love and devotion, and it embraced him in return. That, of course, is all a much longer story for another day.
My father died suddenly at the age of 52 just a few months after my ordination to priesthood in 1982. I remember laying on the floor during the Litany of the Saints at my ordination as I described in “Going My Way,” a Lenten post last year. I was conscious that my father stood on the aisle just a few feet away, and I was struck by the nature of the man whose impact on my life had so miraculously changed. Underneath the millstones of addiction and despair that once plagued him was a singular power that trumped all. It was the sheer courage necessary to be open to the grace of conversion and radical change. The most formative years of my young adulthood and priesthood were spent as a witness to the immensity of that courage. In time, I grew far less scarred by my father’s road to perdition, and far more inspired by his arduous and dogged pursuit of the road back. I have seen other such miracles, and learned long ago to never give up hope for another human being.
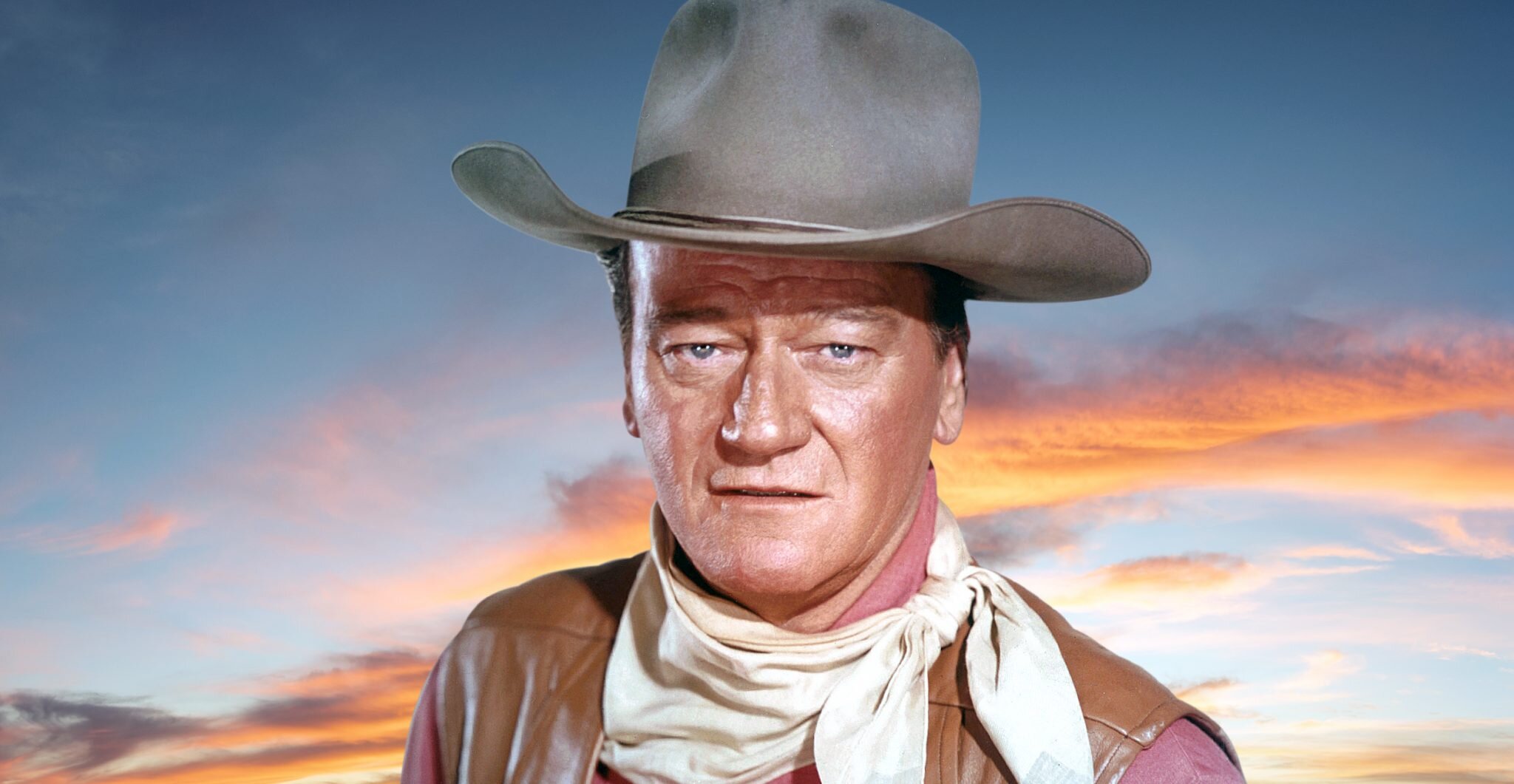
The Conversion of the Duke
A year ago this very week, I wrote “Holidays in the Hoosegow: Thanksgiving With Some Not-So-Just Desserts.” In that post, I mentioned that John Wayne is one of my life-long movie heroes and a man I have long admired. But all that I really ever knew of him was through the roles he played in great westerns like “The Searchers,” “The Comancheros,” “Rio Bravo,” and my all-time favorite historical war epic, “The Longest Day.”
In his lifetime, John Wayne was awarded three Oscars and the Congressional Gold Medal. After his death from cancer in 1979, he was posthumously awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom. But, for me, the most monumental and courageous of all of John Wayne’s achievements was his 1978 conversion to the Catholic faith.
Not many in Hollywood escape the life it promotes, and John Wayne was no exception. The best part of this story is that it was first told by Father Matthew Muñoz, a priest of the Diocese of Orange, California, and John Wayne’s grandson.
Early in his film career in 1933, John Wayne married Josephine Saenz, a devout Catholic who had an enormous influence on his life. They gave birth to four children, the youngest of whom, Melinda, was the mother of Father Matthew Muñoz. John Wayne and Josephine Saenz civilly divorced in 1945 as Hollywood absorbed more and more of the life and values of its denizens.
But Josephine never ceased to pray for John Wayne and his conversion, and she never married again until after his death. In 1978, a year before John Wayne died, her prayer was answered and he was received into the Catholic Church. His conversion came late in his life, but John Wayne stood before Hollywood and declared that the secular Hollywood portrayal of the Catholic Church and faith is a lie, and the truth is to be found in conversion.
That conversion had many repercussions. Not least among them was the depth to which it inspired John Wayne’s 14-year old grandson, Matthew, who today presents the story of his grandfather’s conversion as one of the proudest events of his life and the beginning of his vocation as a priest.
If John Wayne had lived to see what his conversion inspired, I imagine that he, too, would have stood on the aisle, a monument to the courage of conversion, as Matthew lay prostrate on the Cathedral floor praying the Litany of the Saints at priesthood ordination. The courage of conversion is John Wayne’s most enduring legacy.
Pornchai Moontri Takes a Road Less Traveled
The Japanese Catholic novelist, Shusaku Endo, wrote a novel entitled Silence (Monumenta Nipponica, 1969), a devastating historical account of the cost of discipleship. It’s a story of 17th Century Catholic priests who faced torture and torment for spreading the Gospel in Japan. The great Catholic writer, Graham Greene, wrote that Silence is “in my opinion, one of the finest novels of our time.”
Silence is the story of Father Sebastian Rodriguez, one of those priests, and the story is told through a series of his letters. Perhaps the most troubling part of the book was the courage of Father Rodriguez, a courage difficult to relate to in our world. Because of the fear of capture and torture, and the martyrdom of every priest who went before him, Father Rodriguez had to arrive in Japan for the first time by rowing a small boat alone in the pitch blackness of night from the comfort and safety of a Spanish ship to an isolated Japanese beach in 1638 — just 18 years after the Puritan Pilgrims landed the Mayflower at Squanto’s Pawtuxet, half a world away as I describe in “The True Story of Thanksgiving.”
In Japan, however, Father Rodriguez was a pilgrim alone. Choosing to be left on a Japanese beach in the middle of the night, he had no idea where he was, where he would go, or how he would survive. He had only the clothes on his back, and a small traveler’s pouch containing food for a day. I cannot fathom such courage. I don’t know that I could match it if it came down to it.
But I witness it every single day. Most of our readers are very familiar with “Pornchai’s Story,” and with his conversion to Catholicism on Divine Mercy Sunday in 2010. Most know the struggles and special challenges he has faced as I wrote in “Pornchai Moontri, Bangkok to Bangor, Survivor of the Night.”
But the greatest challenge of Pornchai’s life is yet to come. In two years he will have served twenty-two years in prison — more than half his life, and half the original sentence of forty-five years imposed when he was 18 years old. In two years time, if many elements fall into place and he can find legal counsel, Pornchai will have an opportunity to seek some commutation of his remaining sentence based on rehabilitation and other factors.
It is a sort of Catch-22, however. Pornchai could then see freedom at the age of forty for the first time since he was a teen, but it will require entering a world entirely foreign to him. On the day Pornchai leaves prison — whether it is in two years or ten or twenty — he will be immediately taken into custody under the authority of Homeland Security and the Patriot Act, flown to Bangkok, Thailand, and left there alone. It is a daunting, sometimes very frightening future, and I am a witness to the anxiety it evokes.
For every long term prisoner, there comes a point in which prison itself is the known world and freedom is a foreign land. Pornchai has spent more than half his life in prison.
Even I, after seventeen years here, sometimes find myself at the tipping point, that precipice in which a prisoner cannot readily define which feels more like the undiscovered country — remaining in prison or trying to be free. I had a dream one night in which I had won my freedom, but entered a hostile world and Church in which I was a pariah, living alone and homeless in a rented room in hiding, pursued by mobs of angry Catholics. I know well the anxious fears of all the prisons of men.
Pornchai was brought to the United States against his will at the age of eleven. That story is told in deeply moving prose by Pornchai himself in “Pornchai’s Story.” I think we became friends because by the strangeness of grace I knew only too well the experience of having the very foundations of life and family and all security fall out from under me. Pornchai spoke a language that I understood clearly. The transformation of pain and sorrow into the experience of grace is the realm of God, and enduring it to one day lead another out of darkness is a great gift. In the end, who can ever say what is good and what is bad? It is not suffering that is our problem, but rather what we do with it when it finds us.
But what Pornchai faces in the future is daunting. With no opportunity for schooling as an abandoned child in Thailand, he never learned to read and write in Thai and hasn’t heard the Thai language spoken since he was eleven. He remembers little of Thai culture, has no prospects to support himself, no home there, no contacts, and no solace at all. Like Father Rodriguez in Silence, Pornchai will be dropped off in a foreign country, and left to fend for himself with no preparation at all beyond what he can scrape up from behind prison walls in another continent. Welcome to the new America!
Pornchai’s options are limited. He can try to bring about this trauma sooner by seeking commutation of his sentence at an age at which he may still somehow build a life in Thailand. Or he can remain quietly in prison another decade or more, postponing this transition until he is much older, with fewer chances for employment, but perhaps can find connections in Thailand.
These are not great choices. “Pornchai’s Story” got the attention of the Thai government and the Cardinal Archbishop of Bangkok two years ago, but the Thai government has been in chaos since, and the Archbishop has retired. All overtures to both since 2009 have been met by silence.
So in the midst of all this dismal foreboding, and in the face of a future entirely unknown, and perhaps even bleak, Pornchai Moontri became a Catholic. He embraced a faith practiced by less than one percent of the people who will one day be his countrymen again, and in so doing, he piled alienation upon alienation.
And yet this man who has no earthly reason to trust anything to fate, trusts faith itself. I have never met a man more determined to live the faith he has professed than Pornchai Moontri. In the darkness and aloneness of a prison cell night after night for the last two of his twenty years in prison, Pornchai stares down the anxiety of uncertainty, struggles for reasons to believe, and finds them.
I am at a loss for more concrete sources of hope for Pornchai. But like Blessed John Henry Cardinal Newman, whom I have quoted so often, I believe that “I am a link in a chain; a bond of connection between persons.”
Someone out there holds good news for Pornchai — something he can cling to in hope. I await it with as much patience as I can summon. Pornchai awaits it with a singular courage — the courage of conversion that seeks the spring of hope in the winter of despair.